Choosing the right HVAC system for your home is one of the most critical decisions that affects your comfort, energy efficiency, and long-term costs. With so many options available in 2025, selecting the best system can feel overwhelming. This guide will help you understand the different types of HVAC systems, factors to consider, and tips for choosing the right system tailored to your home’s needs.
What is an HVAC System?
An HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system controls the indoor climate by regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality. It keeps your home warm during the winter, cool during the summer, and ensures clean, breathable air throughout the year.
Types of HVAC Systems
Understanding the different types of HVAC systems is essential for making an informed decision. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the most common options:
1. Split HVAC System
A split system consists of two separate units:
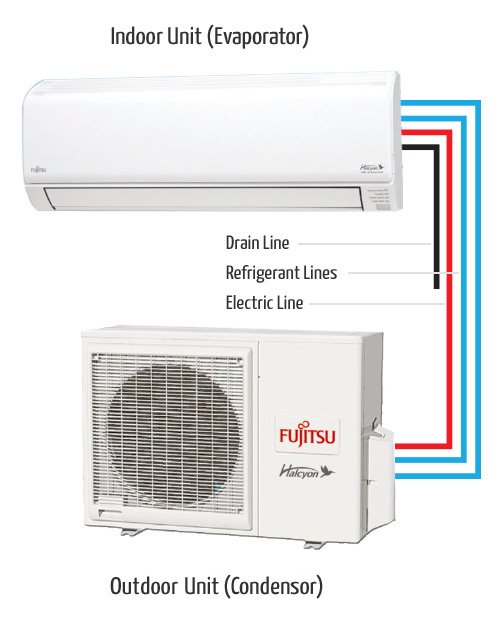
- Indoor Unit: Contains the evaporator coil and blower to circulate conditioned air.
- Outdoor Unit: Houses the compressor and condenser coil that release heat outdoors.
Pros:
- Energy-efficient and reliable.
- Can provide both heating and cooling.
- Available in a variety of sizes and models.
Cons:
- Requires ductwork, increasing installation costs.
- Space-consuming, with separate indoor and outdoor units.
Average Cost: $3,000 – $7,000
Lifespan: 15–20 years
2. Ductless Mini-Split System
A ductless mini-split system operates similarly to a split system but does not require ductwork. It uses an outdoor unit connected to one or more indoor air handlers.
Pros:
- Ideal for homes without existing ducts.
- Offers zone-specific temperature control.
- High energy efficiency with minimal heat loss.
Cons:
- Higher initial cost per unit.
- Less effective for larger homes.
Average Cost: $2,000 – $5,000 per zone
Lifespan: 12–15 years
3. Packaged HVAC System
A packaged system contains all heating and cooling components in one unit, typically installed outside the home or on the roof.
Pros:
- Saves indoor space.
- Easier installation and maintenance.
- Suitable for homes with limited space.
Cons:
- Less energy-efficient than split systems.
- Prone to wear and tear from outdoor exposure.
Average Cost: $4,000 – $8,000
Lifespan: 10–15 years
4. Geothermal Heat Pump System
A geothermal heat pump leverages the earth’s constant underground temperature to provide heating and cooling. It transfers heat to and from the ground using a loop of underground pipes filled with a refrigerant.
Pros:
- Exceptional energy efficiency.
- Environmentally friendly with low carbon emissions.
- Long lifespan and minimal maintenance.
Cons:
- High upfront installation cost.
- Requires sufficient space for underground loops.
Average Cost: $10,000 – $25,000
Lifespan: 25–50 years
5. Hybrid HVAC System
A hybrid system combines an electric heat pump with a gas furnace, automatically switching between the two based on outdoor temperatures.
Pros:
- Optimizes energy use in varying climates.
- Reduces operational costs by switching to the most efficient mode.
Cons:
- Higher initial installation costs.
- Requires regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Average Cost: $6,000 – $12,000
Lifespan: 15–20 years
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an HVAC System
When selecting the right HVAC system for your home, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
1. Climate and Geographic Location
Your local climate plays a critical role in determining the type of HVAC system that best suits your home.
- Hot and Humid Climates: Opt for high SEER-rated air conditioners or heat pumps.
- Cold Climates: Consider a hybrid system or geothermal heat pump for consistent heating.
2. Home Size and Layout
The size and layout of your home determine the heating and cooling capacity required.
- Smaller Homes: A ductless mini-split or packaged system may suffice.
- Larger Homes: A central split system or geothermal heat pump offers better efficiency.
Pro Tip: Improper sizing can lead to inefficiencies, higher energy bills, and frequent breakdowns.
3. Energy Efficiency and SEER Ratings
Look for systems with high SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings.
- SEER Rating: Measures cooling efficiency. Higher SEER ratings reduce energy consumption.
- HSPF Rating: Measures heating efficiency. A higher HSPF means better heating performance.
Recommended Ratings:
- SEER 16+ for air conditioners.
- HSPF 8+ for heat pumps.
4. Initial Cost vs. Long-Term Savings
While higher-efficiency systems have a greater upfront cost, they offer significant savings on energy bills over time. Consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and operational costs.
5. Installation Complexity and Space Requirements
- Ducted Systems: Require adequate space for ductwork installation.
- Ductless Mini-Splits: Ideal for retrofitting homes without ducts.
6. Environmental Impact
If reducing your carbon footprint is a priority, consider geothermal systems or heat pumps, which rely on renewable energy sources and significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions.
How to Calculate the Right Size HVAC System for Your Home
Proper sizing is crucial to avoid issues like short cycling, high energy bills, and inconsistent temperature control. Use the following formula as a starting point:
Manual J Load Calculation Formula:
Cooling Load (BTU) = Square Footage x 20 BTU per sq. ft.
Example:
- Home Size: 1,500 sq. ft.
- Cooling Load: 1,500 x 20 = 30,000 BTU
Pro Tip: Consult an HVAC professional for a detailed Manual J Load Calculation to ensure precise sizing.
Top HVAC Brands to Consider in 2025
When choosing an HVAC system, it’s essential to opt for reputable brands that offer high performance, durability, and comprehensive warranties. Here are some of the best brands to consider:
1. Carrier
Why It’s Best: Known for its innovation, Carrier offers energy-efficient systems with advanced technology.
- SEER Rating: Up to 22
- Ideal For: Split systems and hybrid HVAC setups.
2. Trane
Why It’s Best: Trane systems are highly durable and perform well under extreme weather conditions.
- SEER Rating: Up to 20
- Ideal For: Geothermal heat pumps and packaged systems.
3. Lennox
Why It’s Best: Lennox offers ultra-energy-efficient HVAC systems with innovative smart home integration.
- SEER Rating: Up to 23
- Ideal For: High-efficiency ducted and ductless systems.
4. Daikin
Why It’s Best: Daikin specializes in high-quality ductless mini-split systems and VRF technology.
- SEER Rating: Up to 21
- Ideal For: Zoned cooling and heating solutions.
5. Rheem
Why It’s Best: Rheem offers affordable, reliable systems with solid warranties and good after-sales service.
- SEER Rating: Up to 18
- Ideal For: Budget-friendly HVAC installations.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
1. Choose a Certified HVAC Contractor
A professional installation ensures proper system sizing, correct refrigerant levels, and compliance with local building codes.
2. Schedule Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including cleaning coils, replacing air filters, and checking refrigerant levels, extends the lifespan of your system.
3. Consider Smart Thermostat Integration
A smart thermostat improves energy efficiency by allowing you to schedule heating and cooling cycles based on your daily routine.
Related Article:
👉 Heat Pumps: Pros, Cons, Costs, and Best Brands (2025 Buyer’s Guide)
External Resource for Further Reading:
🔗 U.S. Department of Energy – HVAC System Basics
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right HVAC system for your home requires careful consideration of climate, home size, energy efficiency, and budget. Whether you opt for a split system, mini-split, geothermal heat pump, or hybrid system, ensuring proper installation and regular maintenance will maximize comfort and reduce long-term costs.
Stay tuned to SmartHVACGuide.com for more expert insights and tips on optimizing your home’s HVAC system!

Pingback: Heat Pumps: Pros, Cons, Costs, and Best Brands (2025 Buyer’s Guide) – SmartHVACGuide.com